Enhanced light extraction from free-standing InGaN/GaN light emitters using bio-inspired backside surface structuring
Published in Optics Express, 2017
Recommended citation: Pynn, Christopher D; Chan, Lesley; Gonzalez, Federico Lora; Berry, Alex; Hwang, David; Wu, Haoyang; Margalith, Tal; Morse, Daniel E; DenBaars, Steven P; Gordon, Michael J. (2017). "Enhanced light extraction from free-standing InGaN/GaN light emitters using bio-inspired backside surface structuring." Optics Express. 25(14). 15778-15785. https://opg.optica.org/oe/fulltext.cfm?uri=oe-25-14-15778&id=368404
Abstract
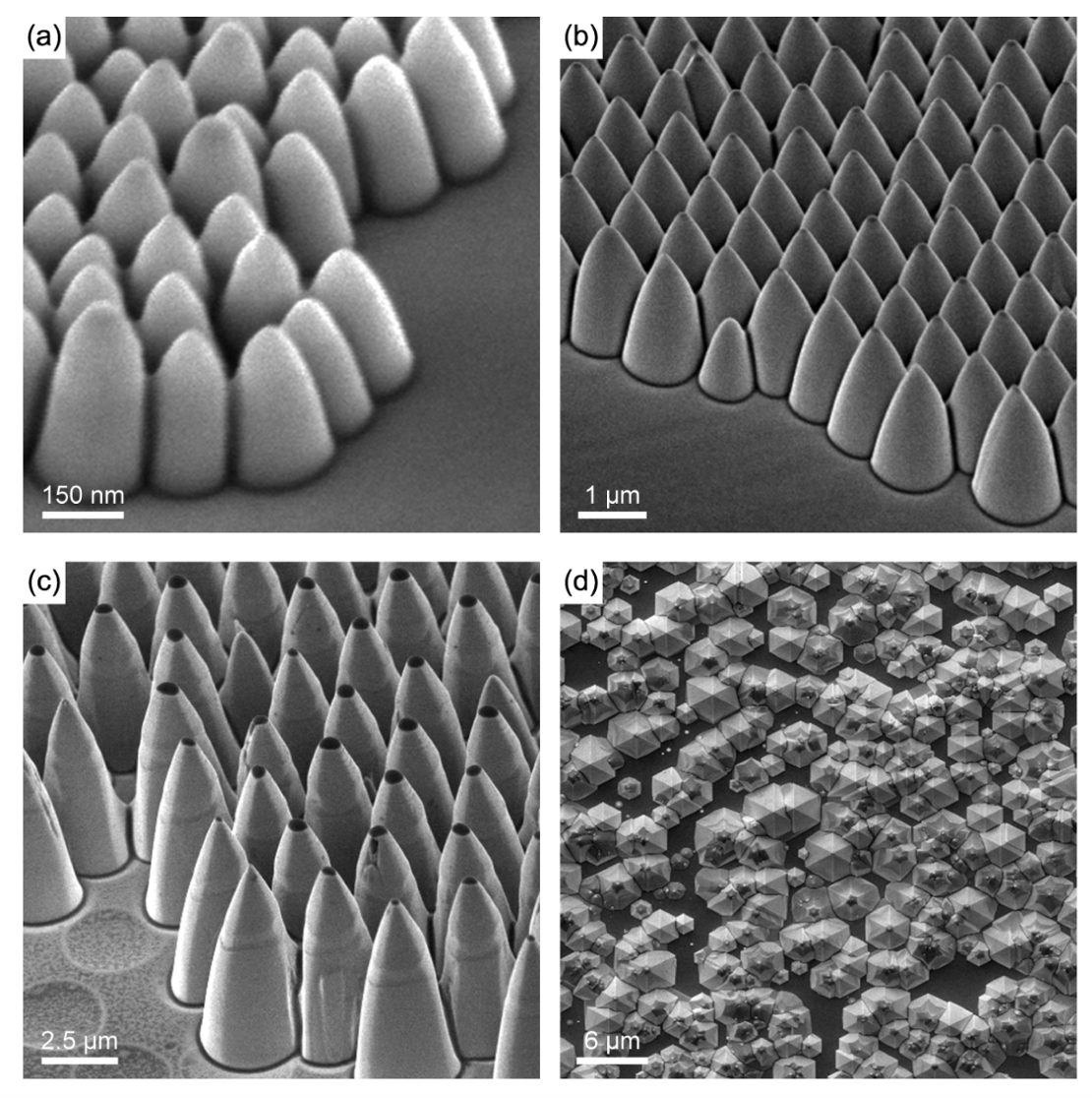
Light extraction from InGaN/GaN-based multiple-quantum-well (MQW) light emitters is enhanced using a simple, scalable, and reproducible method to create hexagonally close-packed conical nano- and micro-scale features on the backside outcoupling surface. Colloidal lithography via Langmuir-Blodgett dip-coating using silica masks (d = 170–2530 nm) and Cl2/N2-based plasma etching produced features with aspect ratios of 3:1 on devices grown on semipolar GaN substrates. InGaN/GaN MQW structures were optically pumped at 266 nm and light extraction enhancement was quantified using angle-resolved photoluminescence. A 4.8-fold overall enhancement in light extraction (9-fold at normal incidence) relative to a flat outcoupling surface was achieved using a feature pitch of 2530 nm. This performance is on par with current photoelectrochemical (PEC) nitrogen-face roughening methods, which positions the technique as a strong alternative for backside structuring of c-plane devices. Also, because colloidal lithography functions independently of GaN crystal orientation, it is applicable to semipolar and nonpolar GaN devices, for which PEC roughening is ineffective.